Finding Lane Lines on Road
Lane detection algorithm using HLS color space, Canny edge detection, and Hough line transform for autonomous vehicle applications.
When we drive, we use our eyes to decide where to go. The lines on the road that show us where the lanes are act as our constant reference for where to steer the vehicle. In this project, I develop an algorithm to detect lane lines automatically.
Programming platform and Libraries: Python and OpenCV.
Methodology
The Pipeline
My pipeline consists of the following steps:
(i) Converting the input image to HLS from RGB
The toHLS() function converts the image to HLS scale and masks the image with yellow and white filters. The HLS domain takes care of the variation in the lighting conditions.
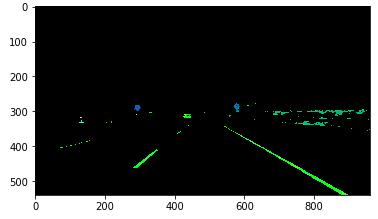
(ii) Converting the HSL masked image to grayscale
The image is further converted into a grayscale image.
(iii) Applying Gaussian Blur
Further, a Gaussian Blur filter with kernel size 15 is used to remove noise.

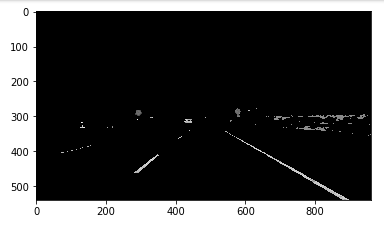
(iv) Perform Canny Edge Detection
Next the grayscaled image is fed into a canny edge detector and edges are obtained. A double threshold is used (low threshold = 100 and high threshold = 200) with low threshold to high threshold ratio between 1/2 to 1/3 as suggested.
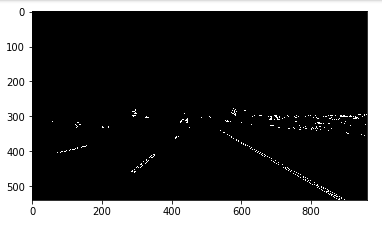
(v) Extract Region of Interest
Edges are detected all over the image, however, the edges that matter are in a particular region therefore the polygonal region is extracted and only those edges that fall in that region are kept while rest are discarded.
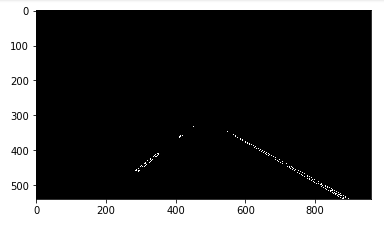
(vi) Draw Hough Lines on the Edge Image
The image with edges is used to draw Hough lines. The function basically converts the points in the image space to lines in the Hough space. For drawing lines I use the modified_draw_lines() function to ensure several line segments are extrapolated/ averaged to one line segment per lane line, also ensuring the smoothness. The raw line segments (more than one per lane line) are broken and need to be averaged as well as extrapolated and for this, I find the slope of each line segment and further classify the points on the line segments to be part of either positive slope or negative slope. Here the line segments with positive slope belong to the right lane line and line segments with negative slope belong to the left lane line. To fit a line, polyfit() with 1 degree is used and further the lane lines are drawn. A global list with a fixed length is maintained to which the coordinates are appended. This helps the algorithm to also keep track of previous points. This way, the broken lines can be extrapolated/ averaged to a single line.
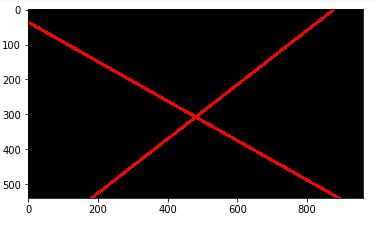
(vii) Extract Region of Interest
Again, the extrapolated lane lines are drawn on the entire image. To avoid this a region of interest masks the image for the lane lines appear only in the region that matters.
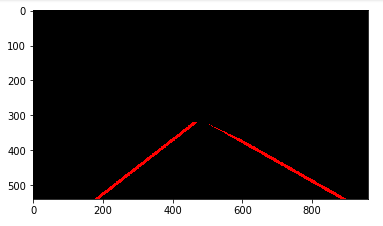
(viii) Weighted Image
The image with extrapolated lines goes on the original image and forms the final image.
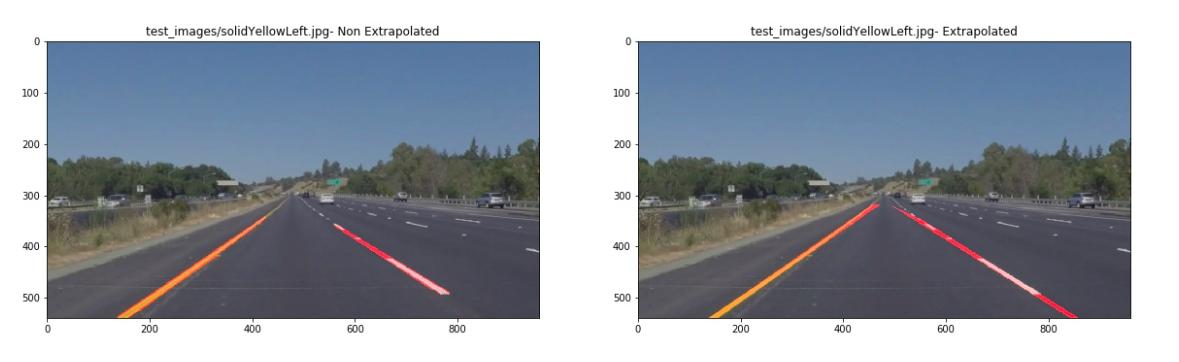
Conclusion
This project is a very primitive way of detecting lane lines. The shortcoming of this project is the need to manually tune a number of parameters that can be done using auto-calibration. Also, the algorithm can be improved using a quadratic curve fitting technique encompassing the edge points. This will provide with better results.
Code Repository: GitHub